Recently, Deng Kaili, a 2020-level master's student specializing in internal medicine from the Medical Department, served as the first author to publish a research paper titled "Chemo-photothermal nanoplatform with diselenide as the key for ferroptosis in colorectal cancer" in the journal "J Control Release" (a top-tier SCI dual-zone journal with an impact factor of 10.8). The main corresponding author of the paper is her advisor, Dr. Zhou Yuping from the First Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University. Co-corresponding authors include Chief Physician Ye Guoliang from the First Affiliated Hospital of Ningbo University and Associate Researcher Xie Na from the Basic Medical College and Forensic Medicine College of West China at Sichuan University. Co-first author of the paper is Dr. Tian Hailong, a graduate student from Sichuan University. Additionally, the research was guided by Professor Huang Canhua from the National Key Laboratory of Biotherapy at Sichuan University.

The study designed a novel camptothecin-loaded nanoparticle to enhance its efficacy against colorectal cancer (CRC) and elucidated its mechanism of action through a pathway that induces ferroptosis combined with photothermal therapy, offering a new strategy for the treatment of mid-to-late stage CRC. Globally, colorectal cancer (CRC) ranks third in both incidence and mortality rates among all types of tumors, with a trend towards affecting younger individuals becoming increasingly apparent. For patients with advanced CRC who are not candidates for surgical treatment, molecular targeted chemotherapy is an emerging therapy. Camptothecin (CPT) is one of the anticancer drugs approved by the U.S. FDA, but its poor water solubility, low biocompatibility, short retention time at the tumor site, and systemic toxicity associated with non-targeted drugs limit its application. This study leveraged a new type of photosensitizer, IR820, to prepare a novel camptothecin-loaded nanoparticle, overcoming its inherent drawbacks and achieving targeted drug delivery and controllable release. It also realized multifunctional synergy between photothermal therapy and chemotherapy. In vivo and in vitro experiments validated its significant clinical efficacy and good safety profile within the body.
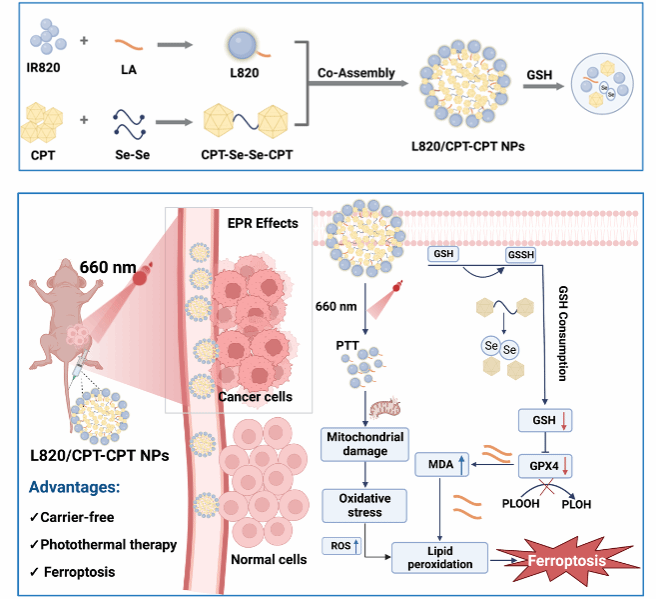
Schematic diagram of photo-thermal response camptothecin-loaded nanomedicine inhibiting colorectal cancer progression through ferroptosis pathway
The research was funded by the Ningbo Municipal High-End Medical Team Major Project (No. 2023020612), the Provincial and Municipal Joint Construction of Key Medical Disciplines (2022-S04), and the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation (LTGD23C040008, LBY23H200006).